并发编程-CompletableFuture
API
提交任务
supplyAsync
// 使用默认内置线程池ForkJoinPool.commonPool(),根据supplier构建执行任务
public static <U> CompletableFuture<U> supplyAsync(Supplier<U> supplier)
// 自定义线程,根据supplier构建执行任务
public static <U> CompletableFuture<U> supplyAsync(Supplier<U> supplier, Executor executor)runAsync
// 使用默认内置线程池ForkJoinPool.commonPool(),根据runnable构建执行任务
public static CompletableFuture<Void> runAsync(Runnable runnable)
// 自定义线程,根据runnable构建执行任务
public static CompletableFuture<Void> runAsync(Runnable runnable, Executor executor)结果转换
thenRun/thenRunAsync
public CompletableFuture<Void> thenRun(Runnable action);
public CompletableFuture<Void> thenRunAsync(Runnable action);
public CompletableFuture<Void> thenRunAsync(Runnable action, Executor executor)thenRun 和thenRunAsync有什么区别呢?
private static final Executor asyncPool = useCommonPool ?
ForkJoinPool.commonPool() : new ThreadPerTaskExecutor();
public CompletableFuture<Void> thenRun(Runnable action) {
return uniRunStage(null, action);
}
public CompletableFuture<Void> thenRunAsync(Runnable action) {
return uniRunStage(asyncPool, action);
}如果你执行第一个任务的时候,传入了一个自定义线程池:
- 调用thenRun方法执行第二个任务时,则第二个任务和第一个任务是共用同一个线程池。
- 调用thenRunAsync执行第二个任务时,则第一个任务使用的是你自己传入的线程池,第二个任务使用的是ForkJoin线程池
TIPS: thenAccept和thenAcceptAsync,thenApply和thenApplyAsync等,它们之间的区别也是这个。
thenApply/thenApplyAsync
public <U> CompletableFuture<U> thenApply(Function<? super T,? extends U> fn)
public <U> CompletableFuture<U> thenApplyAsync(Function<? super T,? extends U> fn)
public <U> CompletableFuture<U> thenApplyAsync(Function<? super T,? extends U> fn, Executor executor)CompletableFuture的thenApply方法表示,第一个任务执行完成后,执行第二个回调方法任务,会将该任务的执行结果,作为入参,传递到回调方法中,并且回调方法是有返回值的。
thenAccept/thenAcceptAsync
public CompletableFuture<Void> thenAccept(Consumer<? super T> action)
public CompletableFuture<Void> thenAcceptAsync(Consumer<? super T> action)
public CompletableFuture<Void> thenAcceptAsync(Consumer<? super T> action, Executor executor)CompletableFuture的thenAccept方法表示,第一个任务执行完成后,执行第二个回调方法任务,会将该任务的执行结果,作为入参,传递到回调方法中,但是回调方法是没有返回值的。
thenAcceptBoth
public <U> CompletableFuture<Void> thenAcceptBoth(CompletionStage<? extends U> other, BiConsumer<? super T, ? super U> action)
public <U> CompletableFuture<Void> thenAcceptBothAsync(CompletionStage<? extends U> other, BiConsumer<? super T, ? super U> action)
public <U> CompletableFuture<Void> thenAcceptBothAsync(CompletionStage<? extends U> other, BiConsumer<? super T, ? super U> action, Executor executor)thenAcceptBoth这一组函数入参包括CompletionStage以及BiConsumer,CompletionStage是JDK1.8新增的接口,在JDK中只有一个实现类:CompletableFuture,所以第一个入参就是CompletableFuture,这一组函数是用来接受两个CompletableFuture的返回值,并将其组合到一起。BiConsumer这个函数式接口有两个入参,并且没有返回值,BiConsumer的第一个入参就是调用方CompletableFuture的执行结果,第二个入参就是thenAcceptBoth接口入参的CompletableFuture的执行结果。所以这一组函数意思是将两个CompletableFuture执行结果合并到一起。
handle
public <U> CompletableFuture<U> handle(BiFunction<? super T, Throwable, ? extends U> fn)
public <U> CompletableFuture<U> handleAsync(BiFunction<? super T, Throwable, ? extends U> fn)
public <U> CompletableFuture<U> handleAsync(BiFunction<? super T, Throwable, ? extends U> fn, Executor executor)CompletableFuture的handle方法表示,某个任务执行完成后,执行回调方法,并且是有返回值的;
并且handle方法返回的CompletableFuture的result是回调方法执行的结果。
同时如果有异常,需要手动处理异常。
thenCombine
public <U,V> CompletableFuture<V> thenCombine(CompletionStage<? extends U> other, BiFunction<? super T,? super U,? extends V> fn)
public <U,V> CompletableFuture<V> thenCombineAsync(CompletionStage<? extends U> other, BiFunction<? super T,? super U,? extends V> fn)
public <U,V> CompletableFuture<V> thenCombineAsync(CompletionStage<? extends U> other, BiFunction<? super T,? super U,? extends V> fn, Executor executor)thenCombine这一组函数和thenAcceptBoth类似,入参都包含一个CompletionStage,也就是CompletableFuture对象,意思也是组合两个CompletableFuture的执行结果,不同的是thenCombine的第二个入参为BiFunction,该函数式接口有两个入参,同时有一个返回值。所以与thenAcceptBoth不同的是,thenCombine将两个任务结果合并后会返回一个全新的值作为出参。
thenCompose
public <U> CompletableFuture<U> thenCompose(Function<? super T, ? extends CompletionStage<U>> fn)
public <U> CompletableFuture<U> thenComposeAsync(Function<? super T, ? extends CompletionStage<U>> fn)
public <U> CompletableFuture<U> thenComposeAsync(Function<? super T, ? extends CompletionStage<U>> fn, Executor executor)thenCompose方法会在某个任务执行完成后,将该任务的执行结果,作为方法入参,去执行指定的方法。
该方法会返回一个新的CompletableFuture实例
- 如果该CompletableFuture实例的result不为null,则返回一个基于该result新的CompletableFuture实例;
- 如果该CompletableFuture实例为null,然后就执行这个新任务
回调方法
whenComplete
public CompletableFuture<T> whenComplete(BiConsumer<? super T, ? super Throwable> action)
public CompletableFuture<T> whenCompleteAsync(BiConsumer<? super T, ? super Throwable> action)
public CompletableFuture<T> whenCompleteAsync(BiConsumer<? super T, ? super Throwable> action, Executor executor)CompletableFuture的whenComplete方法表示,某个任务执行完成后,执行的回调方法,无返回值;
并且whenComplete方法返回的CompletableFuture的result是上个任务的结果。
异常处理
exceptionally
public CompletableFuture<T> exceptionally(Function<Throwable, ? extends T> fn)exceptionally是用来处理异常的,当任务抛出异常后,可以通过exceptionally来进行处理,也可以选择使用handle来进行处理,不过两者有些不同,hand是用来处理上一个任务的结果,如果有异常情况,就处理异常。而exceptionally可以放在CompletableFuture处理的最后,作为兜底逻辑来处理未知异常。
获取结果
AllOf
public static CompletableFuture<Void> allOf(CompletableFuture<?>... cfs)所有任务都执行完成后,才执行 allOf返回的CompletableFuture。
如果任意一个任务异常,allOf的CompletableFuture,执行get方法,会抛出异常
AnyOf
public static CompletableFuture<Object> anyOf(CompletableFuture<?>... cfs)任意一个任务执行完,就执行anyOf返回的CompletableFuture。
如果执行的任务异常,anyOf的CompletableFuture,执行get方法,会抛出异常
get/getNow/join
public T get() throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException
public T get(long timeout, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException, TimeoutException
public T getNow(T valueIfAbsent)
public T join()get方法一个是不带超时时间的,一个是带有超时时间的。
getNow方法则是立即返回结果,如果还没有结果,则返回默认值,也就是该方法的入参。
join方法是不带超时时间的等待任务完成。
使用场景
创建异步任务
| 描述 | 是否支持返回值 | |
|---|---|---|
| supplyAsync | 执行CompletableFuture任务 | 支持 |
| runAsync | 执行CompletableFuture任务 | 不支持 |
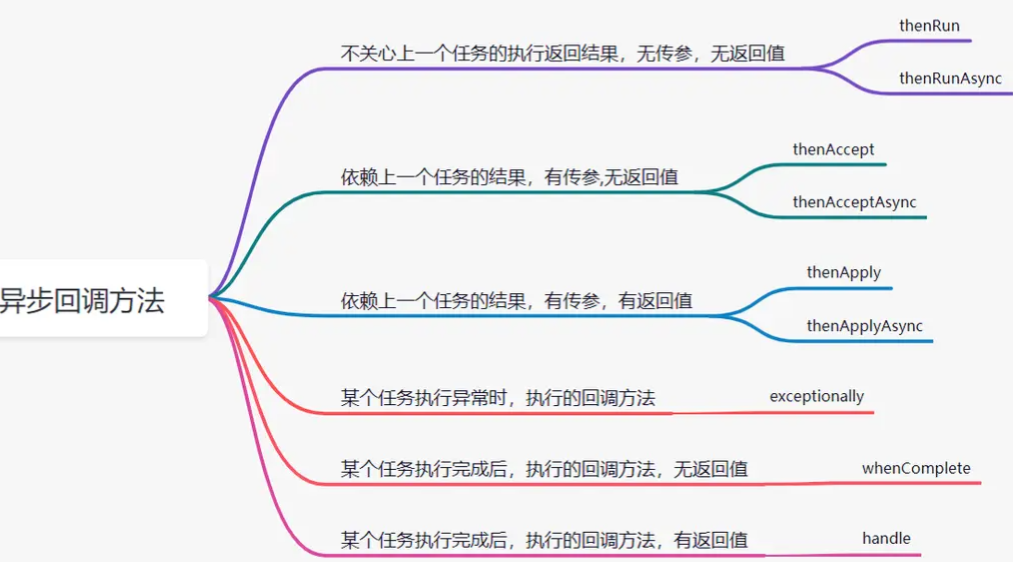
任务异步回调
多任务组合
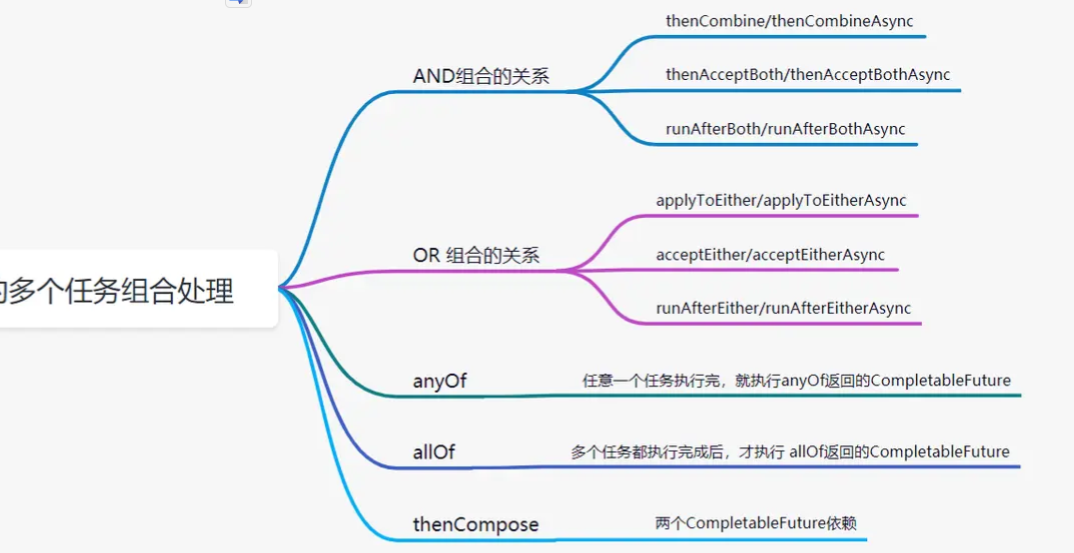
| CompletableFuture | 作用 | 区别 |
|---|---|---|
| AND组合关系 | 将两个CompletableFuture组合起来,只有这两个都正常执行完了,才会执行某个任务 | |
| thenCombine | 将两个任务的执行结果作为方法入参,传递到指定方法中,且有返回值 | |
| thenAcceptBoth | 将两个任务的执行结果作为方法入参,传递到指定方法中,且无返回值 | |
| runAfterBoth | 不会把执行结果当做方法入参,且没有返回值。 | |
| OR 组合关系 | 将两个CompletableFuture组合起来,只要其中一个执行完了,就会执行某个任务 | |
| applyToEither | 会将已经执行完成的任务,作为方法入参,传递到指定方法中,且有返回值 | |
| acceptEither | 会将已经执行完成的任务,作为方法入参,传递到指定方法中,且无返回值 | |
| runAfterEither | 不会把执行结果当做方法入参,且没有返回值。 | |
| AnyOf | ||
| AllOf | ||
| thenCompose |
使用注意事项
1. Future需要获取返回值,才能获取异常信息
ExecutorService executorService = new ThreadPoolExecutor(5, 10, 5L,
TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(10));
CompletableFuture<Void> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
int a = 0;
int b = 666;
int c = b / a;
return true;
},executorService).thenAccept(System.out::println);
//如果不加 get()方法这一行,看不到异常信息
future.get();Future需要获取返回值,才能获取到异常信息。如果不加 get()/join()方法,看不到异常信息。使用的时候考虑是否
加try...catch...或者使用exceptionally方法。
2. CompletableFuture的get()方法是阻塞的。
CompletableFuture的get()方法是阻塞的,如果使用它来获取异步调用的返回值,需要添加超时时间
// 反例
CompletableFuture.get();
// 正例
CompletableFuture.get(5, TimeUnit.SECONDS);3. CompletableFuture默认线程池
CompletableFuture代码中又使用了默认的线程池,处理的线程个数是电脑CPU核数-1。大量请求过来的时候,处理逻辑复杂的话,响应会很慢。一般建议使用自定义线程池,优化线程池配置参数。
当自定义线程池拒绝策略是DiscardPolicy或者DiscardOldestPolicy,当线程池饱和时,会直接丢弃任务,不会抛弃异常。
因此建议,CompletableFuture线程池策略最好使用AbortPolicy,然后耗时的异步线程,做好线程池隔离。
测试用例
商品详情页
@Service
public class ItemServiceImpl implements ItemService {
@Autowired
private GmallPmsFeign pmsFeign;
@Autowired
private GmallSmsFeign smsFeign;
@Autowired
private GmallWmsFeign wmsFeign;
@Autowired
private ThreadPoolExecutor threadPoolExecutor;
@Override
public ItemVO loadData(Long skuId) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
ItemVO itemVO = new ItemVO();
// 1. 获取sku的基本信息
// 后续获取sku的促销信息、spu的销售属性和spu详情信息(需要sku中的spuId)都需要skuInfoEntity
// supplyAsync有返回值
// runAsync无返回值
// 所以这里需要使用supplyAsync
CompletableFuture<SkuInfoEntity> skuFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
Resp<SkuInfoEntity> skuInfoEntityResp = this.pmsFeign.querySkuById(skuId);
SkuInfoEntity skuInfoEntity = skuInfoEntityResp.getData();
if (skuInfoEntity != null) {
BeanUtils.copyProperties(skuInfoEntity, itemVO);
}
return skuInfoEntity;
}, threadPoolExecutor);
// 2. 获取sku的图片信息
CompletableFuture<Void> skuImageFuture = CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {
Resp<List<SkuImagesEntity>> listResp = this.pmsFeign.queryImagesBySkuId(skuId);
List<SkuImagesEntity> images = listResp.getData();
if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(images)) {
List<String> imageUrls = images.stream().map(image -> image.getImgUrl()).collect(Collectors.toList());
itemVO.setPics(imageUrls);
}
}, threadPoolExecutor);
// 3. 获取sku的促销信息 TODO
// 4. 获取spu的所有销售属性
// thenAcceptAsync:有参数,无返回
// thenApplyAsync: 有参数,有返回
// 后续spu详情也需要skuInfoEntity中的spuId,所以这里使用thenApplyAsync
CompletableFuture<SkuInfoEntity> spuFuture = skuFuture.thenApplyAsync(skuInfoEntity -> {
Resp<List<SkuSaleAttrValueEntity>> skuSaleAttrValueResp = this.pmsFeign.querySkuSaleAttrValueBySpuId(skuInfoEntity.getSpuId());
List<SkuSaleAttrValueEntity> skuSaleAttrValueEntities = skuSaleAttrValueResp.getData();
itemVO.setSaleAttrs(skuSaleAttrValueEntities);
return skuInfoEntity;
}, threadPoolExecutor);
// 5. 获取规格参数组及组下的规格参数 TODO
// 6. spu详情 TODO
CompletableFuture<Void> future = CompletableFuture.allOf(skuFuture, skuImageFuture, spuFuture);
// 阻塞主进程,等待子进程全部执行完毕!
future.get();
return itemVO;
}
}@Service
public class ItemServiceImpl implements ItemService {
@Autowired
private GmallPmsFeign pmsFeign;
@Autowired
private GmallSmsFeign smsFeign;
@Autowired
private GmallWmsFeign wmsFeign;
@Autowired
private ThreadPoolExecutor threadPoolExecutor;
@Override
public ItemVO loadData(Long skuId) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
ItemVO itemVO = new ItemVO();
// 1. 获取sku的基本信息
// 后续获取sku的促销信息、spu的销售属性和spu详情信息(需要sku中的spuId)都需要skuInfoEntity
// supplyAsync有返回值
// runAsync无返回值
// 所以这里需要使用supplyAsync
CompletableFuture<SkuInfoEntity> skuFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
Resp<SkuInfoEntity> skuInfoEntityResp = this.pmsFeign.querySkuById(skuId);
SkuInfoEntity skuInfoEntity = skuInfoEntityResp.getData();
if (skuInfoEntity != null) {
BeanUtils.copyProperties(skuInfoEntity, itemVO);
}
return skuInfoEntity;
}, threadPoolExecutor);
// 2. 获取sku的图片信息
CompletableFuture<Void> skuImageFuture = CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {
Resp<List<SkuImagesEntity>> listResp = this.pmsFeign.queryImagesBySkuId(skuId);
List<SkuImagesEntity> images = listResp.getData();
if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(images)) {
List<String> imageUrls = images.stream().map(image -> image.getImgUrl()).collect(Collectors.toList());
itemVO.setPics(imageUrls);
}
}, threadPoolExecutor);
// 3. 获取sku的促销信息 TODO
// 4. 获取spu的所有销售属性
// thenAcceptAsync:有参数,无返回
// thenApplyAsync: 有参数,有返回
// 后续spu详情也需要skuInfoEntity中的spuId,所以这里使用thenApplyAsync
CompletableFuture<SkuInfoEntity> spuFuture = skuFuture.thenApplyAsync(skuInfoEntity -> {
Resp<List<SkuSaleAttrValueEntity>> skuSaleAttrValueResp = this.pmsFeign.querySkuSaleAttrValueBySpuId(skuInfoEntity.getSpuId());
List<SkuSaleAttrValueEntity> skuSaleAttrValueEntities = skuSaleAttrValueResp.getData();
itemVO.setSaleAttrs(skuSaleAttrValueEntities);
return skuInfoEntity;
}, threadPoolExecutor);
// 5. 获取规格参数组及组下的规格参数 TODO
// 6. spu详情 TODO
CompletableFuture<Void> future = CompletableFuture.allOf(skuFuture, skuImageFuture, spuFuture);
// 阻塞主进程,等待子进程全部执行完毕!
future.get();
return itemVO;
}
}@Override // SkuInfoServiceImpl
public SkuItemVo item(Long skuId) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
SkuItemVo skuItemVo = new SkuItemVo();
CompletableFuture<SkuInfoEntity> infoFutrue = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
//1 sku基本信息
SkuInfoEntity info = getById(skuId);
skuItemVo.setInfo(info);
return info;
}, executor);
CompletableFuture<Void> ImgageFuture = CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {
//2 sku图片信息
List<SkuImagesEntity> images = imagesService.getImagesBySkuId(skuId);
skuItemVo.setImages(images);
}, executor);
CompletableFuture<Void> saleAttrFuture =infoFutrue.thenAcceptAsync(res -> {
//3 获取spu销售属性组合 list
List<ItemSaleAttrVo> saleAttrVos = skuSaleAttrValueService.getSaleAttrsBuSpuId(res.getSpuId());
skuItemVo.setSaleAttr(saleAttrVos);
},executor);
CompletableFuture<Void> descFuture = infoFutrue.thenAcceptAsync(res -> {
//4 获取spu介绍
SpuInfoDescEntity spuInfo = spuInfoDescService.getById(res.getSpuId());
skuItemVo.setDesc(spuInfo);
},executor);
CompletableFuture<Void> baseAttrFuture = infoFutrue.thenAcceptAsync(res -> {
//5 获取spu规格参数信息
List<SpuItemAttrGroup> attrGroups = attrGroupService.getAttrGroupWithAttrsBySpuId(res.getSpuId(), res.getCatalogId());
skuItemVo.setGroupAttrs(attrGroups);
}, executor);
// 6.查询当前sku是否参与秒杀优惠
CompletableFuture<Void> secKillFuture = CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {
R skuSeckillInfo = seckillFeignService.getSkuSeckillInfo(skuId);
if (skuSeckillInfo.getCode() == 0) {
SeckillInfoVo seckillInfoVo = skuSeckillInfo.getData(new TypeReference<SeckillInfoVo>() {});
skuItemVo.setSeckillInfoVo(seckillInfoVo);
}
}, executor);
// 等待所有任务都完成再返回
CompletableFuture.allOf(ImgageFuture,saleAttrFuture,descFuture,baseAttrFuture,secKillFuture).get();
return skuItemVo;
}参考文档
编程老司机带你玩转 CompletableFuture 异步编程
CompletableFuture详解 |Java 开发实战
